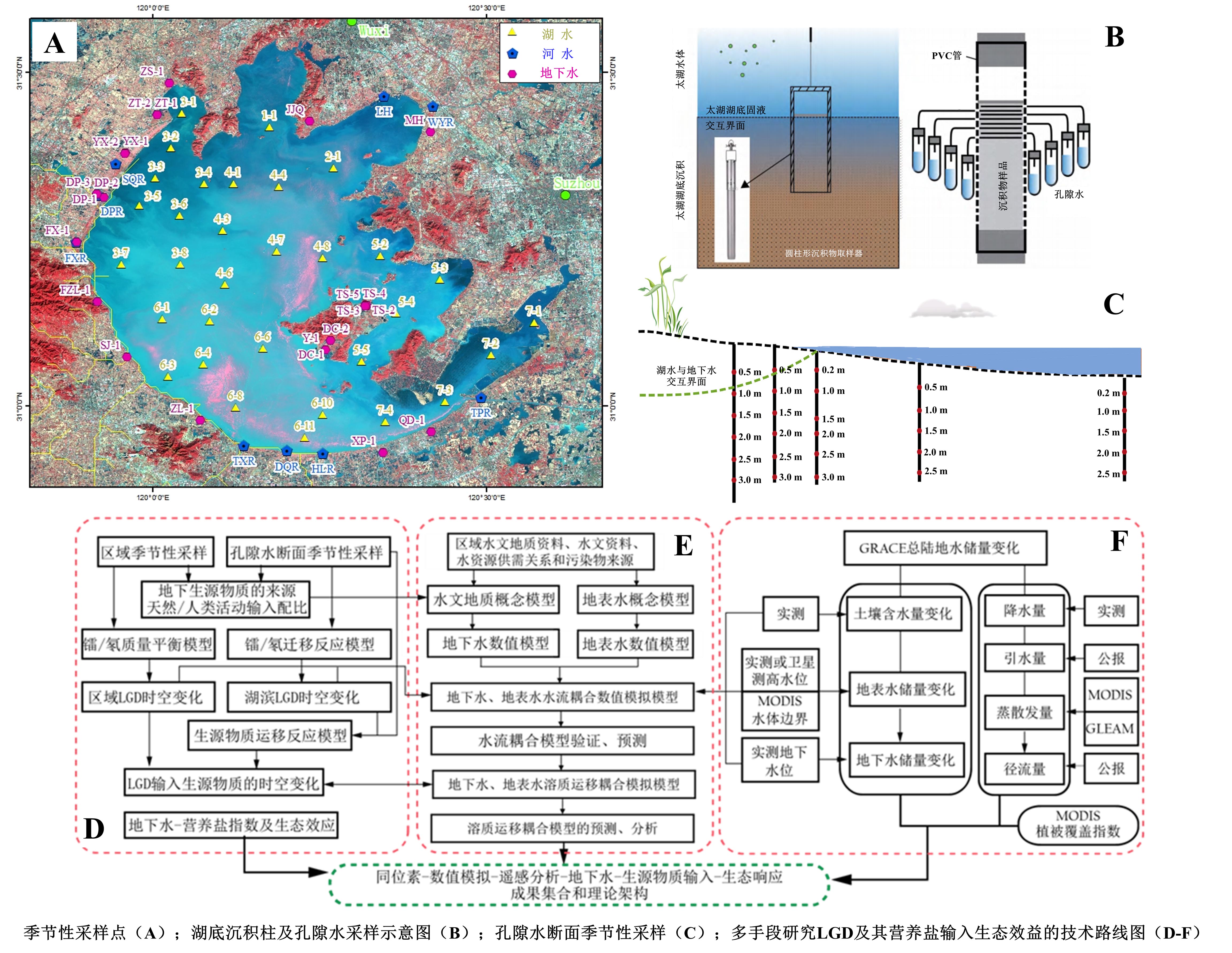
Lake Taihu locates in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and is the third largest freshwater lake in China. With the rapid economic development and increasing urbanization in YRD, Lake Taihu has suffered from serious environmental and ecological issues, such as eutrophication and algae outbreaks. River input and sediments diffusion with anthropogenic sewage and fertilizer are thought to be responsible for these problems and have been primarily targeted in traditional water resource remediation and improvement. On the other hand, the widely-distributed and well-developed groundwater around Lake Taihu may be another nutrition source, because the nutrition could accumulate in groundwater due to the infiltration of sewage and the diffusion from fertilized soil. Therefore, the potential influences from groundwater and LGD need to be clarified, but related study is quite limited.
The programme is proposed to study the interactions between groundwater and lake water, and aims to figure out the environmental and ecological effects of groundwater and lacustrine groundwater discharge (LGD). Firstly, long-term observation station of groundwater will be established, and information about water table center and water level will be recorded. Secondly, isotopic method will be used synthetically, including stable isotopes of hydrogen/oxygen and carbon/nitrogen as well as radioactivity isotopes of radium and radon, to identify the sources of groundwater and nutrition. Thirdly, combined with the technology of gravity satellite remote sensing, a series of models could be established, such as numerical model of groundwater and migration/interaction model of lakeshore area. Lastly, based on the data and the result, the environmental and ecological effects of LGD and its nutrition input will be discussed, and the mechanism of eutrophication and algae outbreaks in Lake Taihu could be further studied. The programme could not only effectively fill the research gap of LGD in China, but also provides more scientific and theoretical support for water resources rehabilitation and management.